Not known Details About Motors, EV West - Electric Vehicle Parts, Components, EVSE
Our KBM™ Series Frameless Motors - Kollmorgen Diaries
Synchronous electric motor powered by an inverter The motor from a 3. 5 in floppy disk drive. The coils, set up radially, are made from copper wire coated with blue insulation. The rotor (upper right) has actually been eliminated and turned upside-down. The grey ring inside its cup is a permanent magnet.
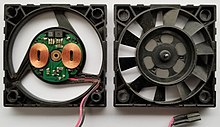
DC brushless ducted fan. View Details on the printed circuit board interact with six round long-term magnets in the fan assembly. A brushless DC electrical motor (BLDC motor or BL motor), also referred to as an electronically commutated motor (ECM or EC motor) or synchronous DC motor, is a concurrent motor using a direct present (DC) electric power supply.
The controller adjusts the stage and amplitude of the DC current pulses to manage the speed and torque of the motor. This control system is an alternative to the mechanical commutator (brushes) used in numerous traditional electrical motors. The construction of a brushless motor system is usually comparable to a irreversible magnet concurrent motor (PMSM), but can also be a changed unwillingness motor, or an induction (asynchronous) motor.

A Biased View of What is the Difference Between Brushed and Brushless DC

The advantages of a brushless motor over brushed motors are high power-to-weight ratio, high speed, nearly immediate control of speed (rpm) and torque, high efficiency, and low maintenance. Brushless motors find applications in such locations as computer peripherals (drive, printers), hand-held power tools, and cars varying from model airplane to cars.
Background [modify] Brushed DC motors were invented in the 19th century and are still typical. Brushless DC motors were made possible by the development of solid state electronics in the 1960s. An electrical motor develops torque by keeping the electromagnetic fields of the rotor (the rotating part of the machine) and the stator (the repaired part of the maker) misaligned.
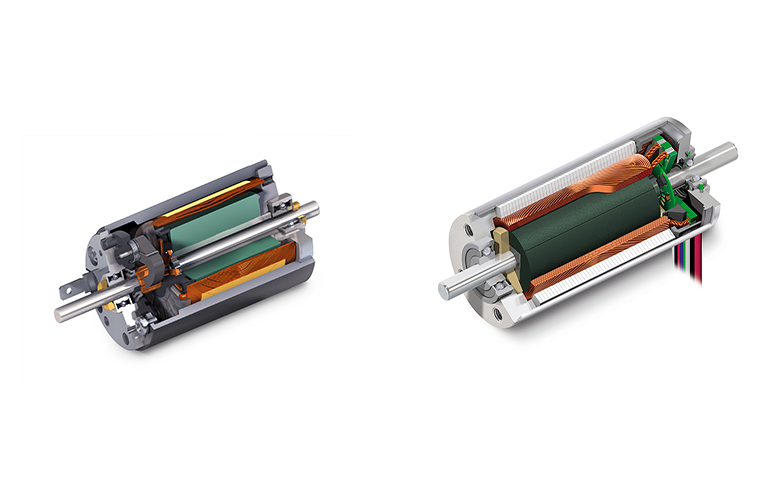
DC running through the wire winding develops the magnetic field, providing the power which runs the motor. The misalignment generates a torque that tries to straighten the fields. As the rotor relocations, and the fields come into positioning, it is needed to move either the rotor's or stator's field to preserve the misalignment and continue to produce torque and movement.
UNDER MAINTENANCE